- Exponential expansion of the human population comes with environmental concerns
- Growth comes with resulting demands for resources has either caused or intensified many environmental issues including deforestation, the depletion of fish reserves, species loss, over-zealous extraction be use of fossil fuel resources, and climate change
- Sustainable Population: population that can survive over thousands of years without running out of resources or damaging its environmental niche
Urbanization:

- More than 80% of Canadians now live in urban areas
- Migration occurs for several reasons
- Farming depends on unpredictable environmental conditions also industrialization of agriculture has reduced the number of small and medium sized farms
- Rural labour market has reduced this people move into cities to search for other economic opportunities
- As cities push outwards to accommodate their ever-growing populations, tremendous pressure is put on the land that is used to produce food
- Changes in land use affect the water cycle and disturb or destroy
- Asphalt and concrete, reduce the ability of the ground to absorb water
- Emissions from vehicular traffic enter and pollute natural waterways, affecting both water and air quality quality of and urban environment is directly related to the health of its inhabitants
- For example increased demands for transportation and energy create pollution and air quality issues
Feeding The World:

- Causes of world hunger include: natural disasters, conflict, poverty, poor agricultural infrastructure, and over-exploitation of the environment
Food Sources:
- Three general sources-crop lands, rangelands, and ocean fisheries
Two Major Agricultural Systems:
- Industrialized agriculture: growth of food using machines and synthetic fertilizers and pesticides
- Traditional agriculture: growth of food by hand, using natural fertilizers and pesticides
Energy Use in the Human Food Web:
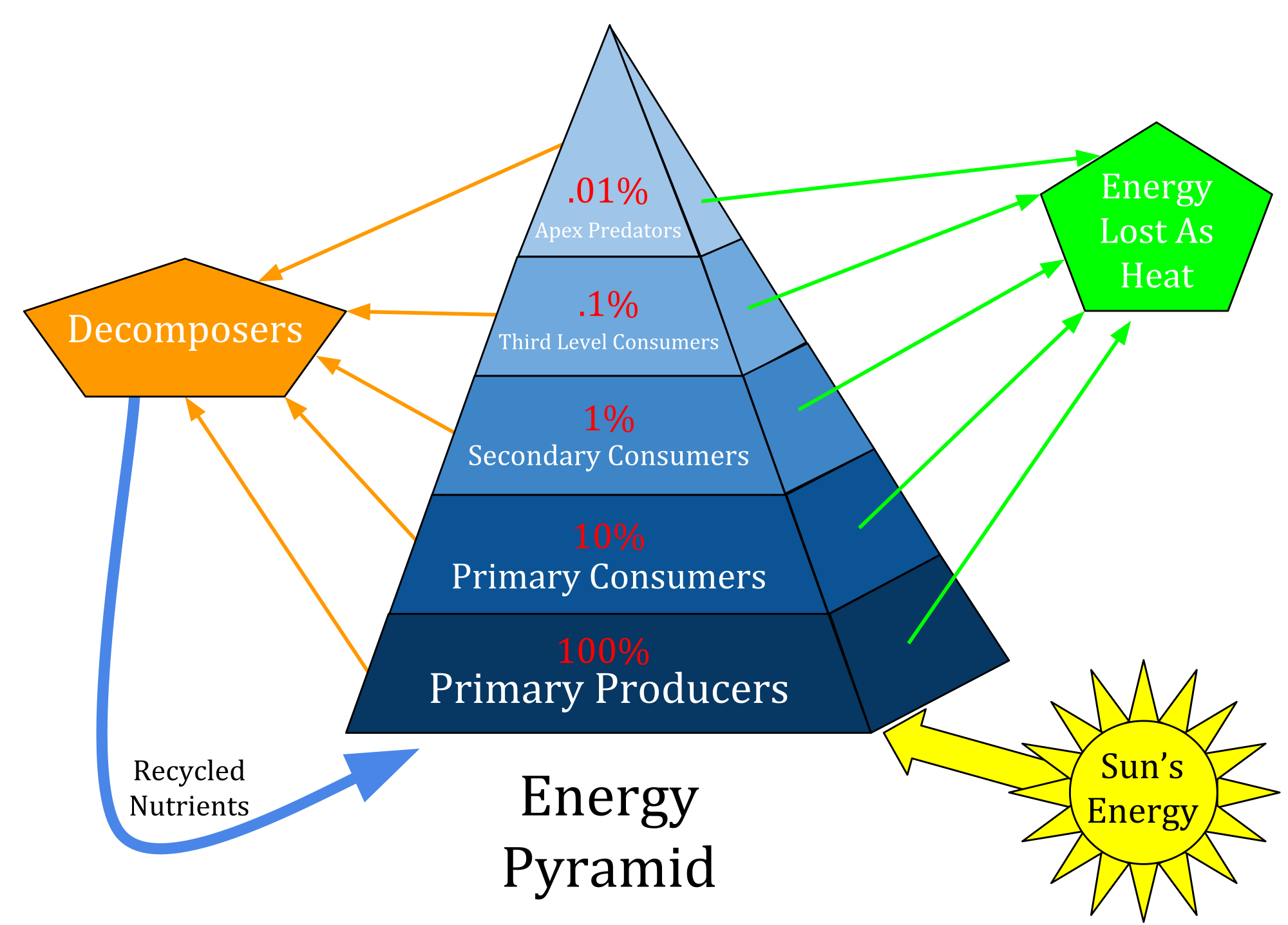
- Energy pyramids: tool that is used by researchers to track the usable energy in a food web
- Tropic level: one level of a food web
- Energy in agriculture can be measured in terms of the energy that goes into producing a unit of food
- Another way is to calculate agricultures ecological footprint
- Food choices we make as consumers can make a difference
- Choosing food sources low on the food pyramid conserves more energy and helps to lessen agriculture's ecological footprint
Threats to Soil:
- Key threats- soil erosion and lost fertility, desertification and salinization (the addition of salt products to the overuse of resources)
- Soil erosion-movement of soil components from one place to another
- Desertification-occurs when the productive potential of arid or semi-arid land falls by 10% or more because of a combination of natural climate change that causes prolonged drought and human activities that reduce or degrade topsoil
- Methods to keep soil moist: irrigation- which involves channeling water to moisten land that does not receive enough rainfall to support agriculture. However irrigation water is a dilute solution of various salts that are picked up as the water flows through soil and rocks, and what is not absorbed leaves a thin crust of dissolved salts in the topsoil.
Sustainable Agriculture:
- growth of food using less energy and fewer resources than industrialized agriculture uses
- Organic agriculture- method of growing food without using synthetic fertilizers and pesticides
Aquatic Food Sources: The World's Fisheries
Water Supplies and Demands:

- Water is one of our most poorly managed resources
- Worlds freshwater supply is continuously collected, purified, recycled, and redistributed in the solar-powered hydrologic cycle
- Causes of water pollution: including agricultural runoff, sewage and wastewater, industrial waste, atmospheric deposition, marine dumping, oil pollution and radioactive waste
Air Quality and Pollution

- Atmosphere is polluted by burning fossil fuels, forests, garbage, manufacturing emissions and gases released by livestock
- Climate Change: continuing rise in the average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans. Caused by increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, resulting from human activities such as deforestation and the combustion of fossil fuels
- Air pollution can cause many health problems
- Airborne particles can aggravate respiratory illnesses, such as asthma
- Airborne chemicals have also been associated with low birth weight babies and infant lung infections
- Ways to curb air pollution- cleaning up industrial emissions, as well as using greener energy sources, burn less gasoline and use less electricity to reduce our global footprint

No comments:
Post a Comment